Palmar
Flexion when Worksurface is Too High
 What is Palmar
Flexion?
What is Palmar
Flexion?
The natural position of the hand when extended is with the
fingertips level with or slightly below the wrist. When the hand
is angled downward from this position, the resulting position is
called
palmar flexion. This greatly reduces blood
flow through the wrist and can quickly cause pain, fatigue and
numbness.
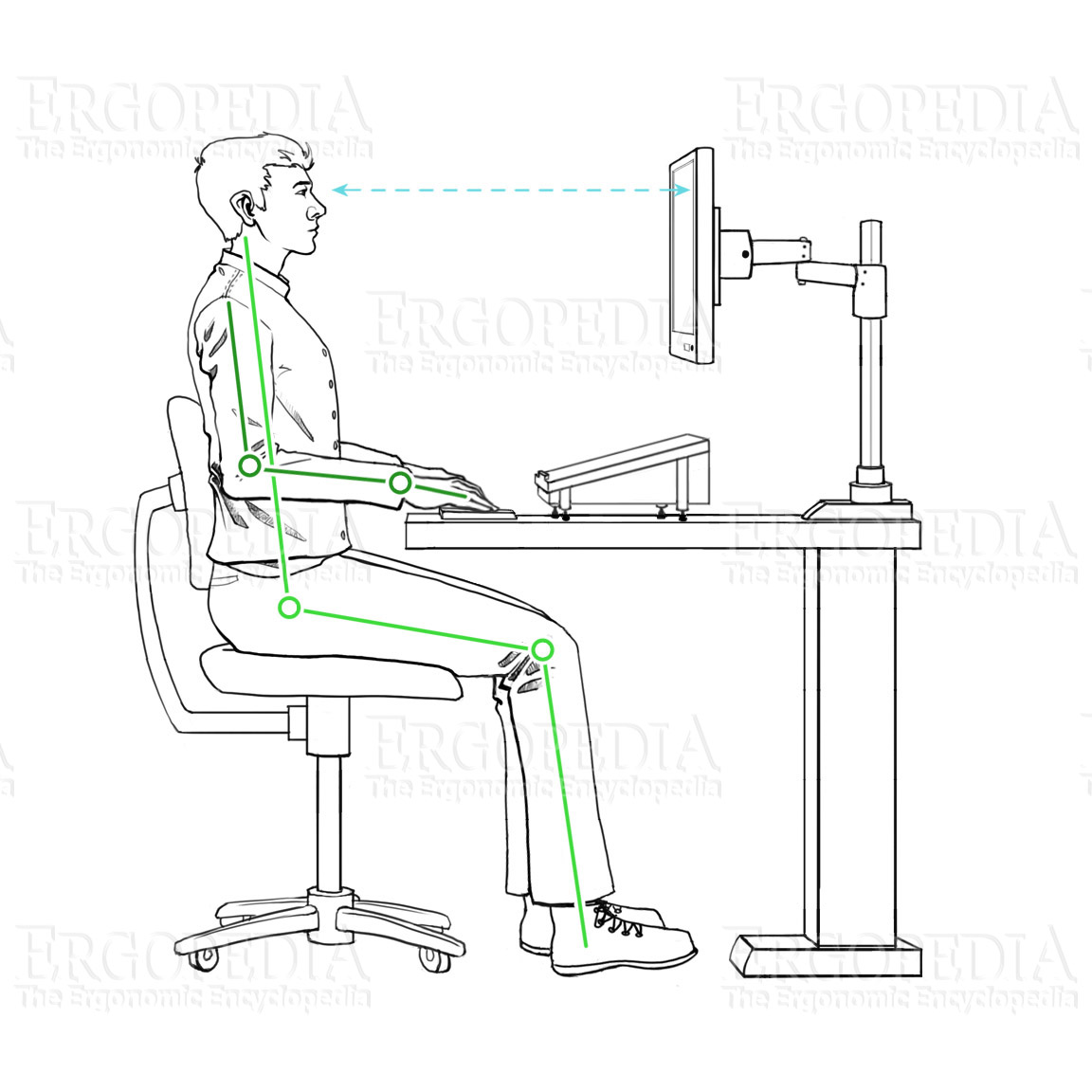
Most standard desks are 29" high, which is (on average) the
ideal height for someone who is 6' 0" tall. Individuals
shorter than this who make no other modifications and place the
keyboard and mouse on the desktop will be in a position of
palmar flexion. The image at right shows the ideal
positioning for a user, with no modifications to the
workstation.
Why is Palmar Flexion a Risk Factor?
The position of Palmar Flexion reduces blood flow through both
constriction of the ulnar artery as well as the accompanying
sustained muscle tension. The result is a significant reduction
in blood flow to the muscles of the hand and forearm. The
median
nerve also runs through the
carpal tunnel in
the wrist, and when adopting a position of Palmar Flexion the
span of this tunnel is compressed. The accompanying increase of
pressure on this nerve can lead to
Carpal
Tunnel Syndrome. It can also eventually lead to
Dupuytren's Contracture (
Palmar Fibromatosis),
which reduces the ability of the fingers to fully extend.
How Much Palmar Flexion is "OK" and not a Risk Factor?
For most individuals, even a minimal amount of Palmar Flexion
will cause some discomfort and is a potential risk factor.
What are the Symptoms of "Too Much" Palmar Flexion?
Typically the initial indication will be a lump in the palm of
the hand near the base of the fingers, which can present with or
without accompanying pain. As it progresses, a reduction
in the flexibility (especially when using the extensor muscles
to open the hand fully) and pain in the fingers can occur.
How can the Choice of Workstation Help to Reduce Palmar
Flexion?
Adjustable
Height or Sit Stand Workstations can be adjusted to the
correct height for the user, which will not only reduce but will
eliminate the position of palmar flexion. On worksurfaces
that are too high, the addition of an
Articulating
Keyboard Arm can bring the keyboard and mouse below the
worksurface to the appropriate height for the individual.
What Other Strategies can be used to Reduce Palmar Flexion?
Most chairs have the ability to adjust in height. By raising the
height of the seat, it may be possible to achieve the proper
relative arm height. Note: This will usually also require the
addition of a
Foot
Rest to prevent dangling feet.
Often individuals will adopt positions of Palmar Flexion while
they are asleep (without realizing it). The wearing of a wrist
brace or support while sleeping can prevent accidental adoption
of a position of Palmar Flexion when one is supposed to be at
rest.

 What is Palmar
Flexion?
What is Palmar
Flexion?